Agrifood Tech Hits $16B in 2024, First FDA-Cleared Cultivated Pork Fat, and $20M+ for AI-Driven Crop Development
Also: China signals support for alternative proteins in two key policy documents released before the Two Sessions summit
Hey, welcome to issue #95 of the Better Bioeconomy newsletter. Thanks for being here! 👋🏾
This week, China doubled down on alternative proteins, reinforcing its commitment to food security and biotech-driven innovations. Mission Barns made history as the first company to secure FDA clearance for cultivated pork fat. Meanwhile, global agrifood tech investment reached $16B in 2024, showing signs of stabilization despite a slight dip from last year.
On the innovation front, Decibel Bio raised $12M to advance its epigenetic platform for precision crop trait control, without genetic modification. And in the lab, scientists found that co-culturing algae and bacteria can significantly boost carotenoid production, with major implications for biomanufacturing.
Let’s dig into the latest updates on the intersection of biotech and agrifood!
BIO BUZZ
Products, partnerships, and regulations
🇨🇳 China signals support for alternative proteins in two key policy documents released before the Two Sessions summit
The Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs and the No. 1 Central Document reaffirm China's focus on alternative proteins, linking them to broader goals of food security and bioeconomy growth.
China's five-year agriculture plan advances research in cultivated meat, recombinant proteins, and biotech-driven food sources like fungal and algae proteins. The Ministry of Agriculture is also prioritizing funding for food processing innovations, including microbiomics and AI-driven production.
Although China doesn’t yet have a formal approval process for cultivated meat, regulators are said to be closely watching global developments to shape their own framework. Events like the China-Singapore symposium reflect ongoing efforts to advance cultivated meat production and related technologies.
Source: Green Queen
🇺🇸 Mission Barns becomes the first company to receive regulatory clearance for cultivated pork fat
The California-based company received an FDA ‘no questions’ letter for its cultivated pork fat and is in the final stages of USDA approval. It will debut its products in San Francisco’s Fiorella restaurant chain and Sprouts Farmers Market stores, targeting meatballs and bacon.
This makes Mission Barns the first company to receive regulatory clearance for cell-cultivated pork fat and the third overall to secure US approval for cultivated animal cells (after UPSIDE Foods and GOOD Meat).
The company believes that adding small amounts of cultivated fat to plant-based products will significantly improve taste and texture, attracting consumers dissatisfied with current plant-based meat alternatives.
Source: AgFunder
🇩🇪🇺🇸 Marsapet launched a kibble product for dogs using Calysta’s FeedKind protein derived from gas fermentation
The German pet food company launched MicroBell, a kibble product that incorporates Calysta’s FeedKind protein as a key ingredient. FeedKind is a fermentation-derived protein that uses methane as its carbon and energy source.
Produced through gas fermentation, FeedKind relies on naturally occurring microbes to convert oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon into a highly digestible, non-GMO protein. It contains 71% crude protein and 9% crude fat, making it a nutrient-dense option with a well-balanced amino acid profile.
Designed for optimal nutrient absorption and efficient feed conversion, FeedKind is also grain-free, making it a suitable choice for dogs with sensitive stomachs or allergies.
Source: Green Queen
🇺🇸 Pow.Bio launched a 25,000 sq ft FDA-registered facility to help companies scale ingredient production with continuous fermentation
The new facility in California helps clients transition from small experiments to producing hundreds of kilos of ingredients. Unlike traditional batch fermentation, which needs frequent sterilization, Pow.Bio’s continuous method maintains optimal conditions for microbes, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Pow.Bio’s platform separates microbial growth from product formation, helping reduce contamination and genetic drift. The system also enhances process control through advanced software and automation.
Built for easy integration, the platform allows co-packers to shift from batch to continuous fermentation with minimal investment potentially doubling output while cutting costs.
Source: AgFunder
🇬🇧 New Wave Biotech’s AI-powered optimisation led to significant cost reduction for Multus’ cultivated meat bioprocessing
Through New Wave Biotech's AI-powered optimization, Multus, also based in the UK, reduced the production costs of growth factors by 55%, increased product recovery by 8.6X, decreased processing time by 37.4%, and more than doubled product concentration.
New Wave Biotech’s Bioprocess Foresight platform combined mechanistic modeling and AI to optimize downstream processing. This allowed Multus to achieve cost reductions with only eight datasets.
Following the success of this optimization, Multus plans to expand the optimized process to other product lines. It also intends to use New Wave’s techno-economic analysis functionality to refine cost structures and improve business decisions.
Source: New Wave Biotech
BIO BUCKS
Funding, M&As, and grants
🌏 Global agrifood tech investment reached $16B in 2024 with a 4% decline from 2023, showing signs of leveling out
The US led with $6.6B (+14% YoY), while India climbed to second place with $2.5B (+215% YoY). Other strong performers included the Netherlands (+118%), Finland (+403%), and Japan (+76%), whereas China, the UK, and Spain saw notable declines.
Early-stage funding was the most active, making up 1,556 deals (77%) out of 2,031 total deals. Growth-stage investments made up 12%, later-stage (D+) 4%, and debt financing 7%.
Upstream sectors received 51% of total funding but suffered a 22% YoY drop. Ag Biotechnology, the top-funded category in the upstream sector, attracted $1.9B, though this is a 12% decline from 2023.
Source: AgFunder
🇺🇸 Decibel Bio emerged from stealth with an oversubscribed $12M funding round to advance its epigenetic platform for better plant traits
The California-based plant biotechnology startup enables real-time adjustments to crop traits, like enhancing yield, drought tolerance, and resistance to environmental stress, without modifying genetic material.
The platform allows farmers to trigger stress-response genes to mitigate risks from different conditions, such as drought, heat waves, and excess rainfall. It also fine-tunes growth to boost yield under ideal conditions, offering a new level of flexibility in agriculture.
Decibel Bio’s founding team, with expertise in synthetic biology, epigenomics, and plant physiology, developed their platform at Sound Agriculture. They plan to use the funding to expand partnerships and accelerate commercialization of their platform.
💰 Investors: Breakthrough Energy Ventures, Future Ventures, Bayer, and Syngenta
Source: GlobeNewswire
🇺🇸 Avalo raised $11M Series A for AI crop development platform and partnered with Coca-Cola Europacific Partners to futureproof sugarcane
Avalo’s Gene Discovery by Informationless Perturbation (GDIP) technology accelerates the time to market for new sugarcane varieties from over 12 years to just 5-6 years. Unlike traditional methods that struggle with complex genetics, Avalo’s AI-driven approach identifies genes responsible for key traits with over 90% accuracy.
Its partnership with Coca-Cola aims to make sugarcane farming more sustainable by reducing dependence on nitrogen fertilizers and water, tackling both environmental and economic challenges while lowering scope 3 emissions.
Avalo is not limited to sugarcane. It is also developing drought-resistant cotton, working with partners to establish a US rubber source from dandelions, and designing a fast-growing indoor broccoli variety that matures in 37 days, allowing for up to six harvests per year.
💰 Investors: Germin8 Ventures, Coca-Cola Europacific Partners, Better Ventures, SOSV, Climate Capital, and more.
Source: AgFunder
🇫🇮 Solar Foods secured a €10M grant from Business Finland to scale up gas-fermented protein production
The funding, which is part of the European Commission’s Important Projects of Common European Interest initiative supporting low-carbon technology, follows a €33.6M grant from 2022. The new grant will support regulatory filings, product launches, and pre-engineering for the Factory 02.
Solar Food’s Factory 01, located near Helsinki, has been operational since April 2023 and currently produces 160 tons of Solein annually. The company intends to increase its capacity to 230 tons by 2026.
Aiming for a 12,800-ton-per-year facility, Factory 02's first phase requires €134M investment. It is projected to generate annual revenues of €48–55M and EBITDA margins of 57-62%.
Source: AgFunder
🇨🇦 Canadian Government allocated CAD $1M to advance cellular agriculture research and innovation in the Prairie province
The Government of Canada has allocated CAD $1M through PrairiesCan for the Cellular Agriculture Prairies Ecosystem (CAPE) Project, an initiative led by New Harvest Canada. With matching contributions from regional partners, total funding will reach CAD $2.4M over three years.
The CAPE Project will create a strong research network by integrating academic and industry collaborations. Major educational institutions like the University of Alberta, University of Manitoba, and Lethbridge Polytechnic will contribute to developing biomanufacturing solutions that make use of local agricultural inputs.
As part of the initiative, New Harvest’s fellowship program will expand to Canada, supporting PhD and postdoctoral researchers working on industry-driven challenges. Their focus includes developing sustainable cell culture media and exploring new uses for underutilized crops like canola byproducts.
Source: vegconomist
GEEK ZONE
Scientific research papers
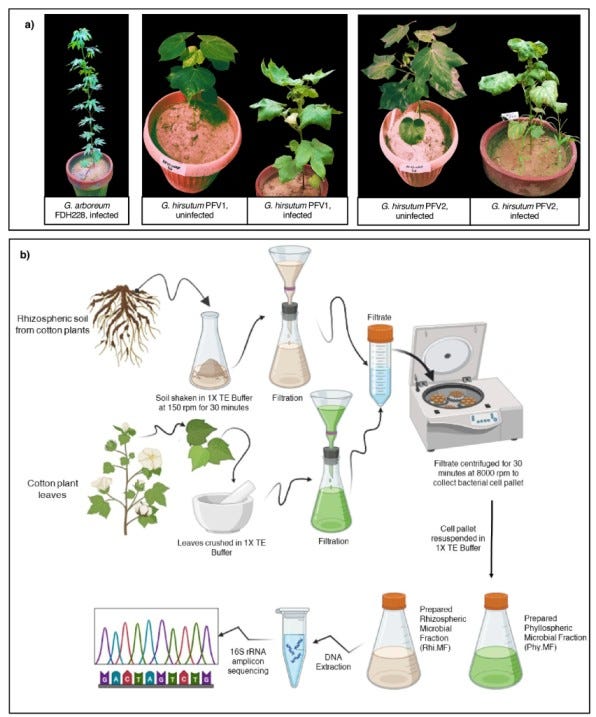
🌱 Microbiota transplantation between cotton species could be more effective than chemical treatments in improving disease resistance
Transferring microbiota, especially from the rhizosphere of Gossypium arboreum (naturally resistant cotton), significantly lowers cotton leaf curl disease symptoms in Gossypium hirsutum (a more susceptible variety). Rhizospheric microbiota transplants worked better than phyllospheric ones and even outperformed exogenous salicylic acid in suppressing disease.
Certain bacterial genera, like Pseudoxanthomonas and Stenotrophomonas, were more common in resistant plants and seemed to help fight off the disease. Key genetic functions, including protein kinases and ATP-binding processes, were upregulated, helping plants better withstand disease pressures.
Instead of relying on chemical treatments, this method uses natural microbial communities to help plants defend themselves. The findings support microbiota transplantation as an environmentally friendly way to improve crop resilience.
Source: Communications Biology (H/T Phy.org)
🦠 Co-culturing algae and bacteria under nitrate-depleted conditions and CO₂ supplementation improved carotenoid production
When grown together, C. saccharophila and Exiguobacterium sp. produced more carotenoids, especially lutein and zeaxanthin. The violaxanthin cycle was more active under CO₂ supplementation, leading to greater conversion of violaxanthin to zeaxanthin, which helps protect cells from oxidative stress.
In the co-culture, sucrose levels were significantly higher than trehalose, whereas the bacterial mono-culture had more trehalose but no sucrose. This shift suggests that the algae-bacteria partnership supports carbon metabolism by prioritizing sucrose for growth and photosynthesis.
Co-culture led to a notable increase in chlorophyll-a and chlorophyll-b, supporting improved photosynthesis. Biomass yield reached 912.17 mg.L⁻¹ under CO₂ supplementation, a clear jump from the nitrate-depleted (546.00 mg.L⁻¹) and nitrate-replete (392.17 mg.L⁻¹) conditions.
Source: World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology
🍅 Novel recombinant protein combining five immune-boosting peptides increased tomato’s resistance to fungal infections
Researchers developed SlRP5, a recombinant protein combining five immune-boosting peptides. It significantly strengthened tomato resistance to the Botrytis cinerea fungus, activating key immune responses like ROS production, MAPK signaling, and callose deposition.
SlRP5 helped limit pathogen damage by reducing MDA and REC levels, markers of cell stress. It also increased key antioxidant enzymes, helping plants manage oxidative stress more effectively. Tomato plants treated with SlRP5 showed better chlorophyll retention and photosynthesis after infection.
Unlike chemical fungicides, SlRP5 stimulates the plant’s immune system, offering an environmentally friendly alternative. It also addresses the cost and stability issues seen with traditional peptide elicitors, making it more viable for large-scale agriculture.
Source: Frontiers in Plant Science
EAR FOOD
Podcast episode of the week
🎧 The indispensable role of techno-economic analysis in bringing climate tech innovations to market
Hosts: Dan Goodwin
Guest: Jesse Lou, CEO of Conductor Labs
A lot of deep tech innovations don’t fail because the science is bad, it’s because the numbers just don’t add up at scale. That’s where techno-economic analysis (TEA) comes in. It helps founders figure out if their technology can actually compete in the real world before they invest years of their lives into it.
It’s easy for innovators to get laser-focused on their specific breakthrough without thinking about how it fits into the bigger picture. However, a breakthrough in one part of the process doesn’t always mean lower overall costs, especially if the downstream steps are still expensive.
The TEA doesn’t have to be perfect to be useful. Even a rough analysis can be valuable. It’s not about nailing every decimal point but about identifying the biggest cost drivers and potential roadblocks early on.
CHECK IT OUT
I'm happy to share that Better Bioeconomy is a Media Partner for HackSummit! 🇨🇭
HackSummit returns to Lausanne on May 15-16, bringing together top climate builders, investors, scientists, and operators to double down on climate deep tech. Across two action-packed days, expect game-changing talks, rapid-fire pitches, hands-on workshops, and city-wide side events to accelerate investment into impact.
💰 Save 20% with discount code "BETTER20" when you book your place here!
GOT A MINUTE?
If you found value in this newsletter, consider sharing it with a friend who might benefit! Or, if someone forwarded this to you, consider subscribing.
This newsletter is free, but if you'd like to support the time and effort behind each issue, a small pledge is always appreciated.
Interested in reaching an engaged, highly niche audience of over 1,600 biotech x agrifood enthusiasts? For sponsorship opportunities, reach out at eshansamaranayake@gmail.com or simply reply to this email.
Got any feedback/suggestion? Drop them here:
Thank you, and have a great day!
Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in this newsletter are my own and do not necessarily reflect those of my employer, affiliates, or any organizations I am associated with.





Correction: I meant to say “$50+ Billion in 2021” for the funding meme, but I only saw that after I sent the email. Sorry!