China's ¥80M Alt Protein Boost, Luxury Cultivated Caviar, and 3 SynBio Acquisitions
Also: Hochland Group and Those Vegan Cowboys have partnered to develop animal-free cheese using microbial casein.
Hey, welcome to issue #89 of the Better Bioeconomy newsletter. Thanks for being here!
If you’re working on (bio)tech-based solutions for sustainable food systems, I’d love to connect. I started this newsletter to meet folks with similar interests, so feel free to reach out to chat on LinkedIn or hop on a call—I’m always happy to discuss ideas and opportunities! 🙂
Let’s dig into the latest updates on the intersection of biotech and agrifood!
BIO BUZZ
🇨🇳 China opened its first alt protein centre for cultivated meat and fermentation-derived products
Beijing's Fengtai District launched the "New Protein Food Science and Technology Innovation Base." The initiative is supported by the public and private sectors, with an ¥80M ($10.9M) investment from the local government and Shounong Food Group.
The centre has advanced facilities, including a 200-litre cell line for cultivated meat and a 2,000-litre microbial protein line. It aims to transition lab research into scalable industrial applications, focusing on cell engineering and synthetic biology. During the opening, the showcased products included microbial protein bars, microbe-fermented tofu meat, and cultivated marbled steak.
Known for its advancements in biomanufacturing, Fengtai District issued policies in May to enhance food industry productivity through resource integration. The Shounong Industrial Park aims to attract scientific research and collaboration, positioning Beijing as a leader in future food technologies.
Source: Green Queen
🇬🇧 Four UK-based centres team up to advance alt protein innovation
The centres — the Bezos Centre for Sustainable Protein (BSCP), Microbial Food Hub, Cellular Agriculture Manufacturing Hub (CARMA), and National Alternative Protein Centre (NAPIC) — have formalized their collaboration with a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU).
The MoU addresses key challenges in alt protein, including high costs, scaling production, and consumer acceptance. It combines research in cellular agriculture, microbial innovation, and plant-based solutions.
All centres launched in the last two years. The initiative highlights the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration for sustainable food solutions through partnerships and workshops. The centres aim to use alt proteins to tackle global challenges like climate change, food security, and public health.
Source: vegconomist
🇩🇪🇧🇪 Hochland Group and Those Vegan Cowboys have partnered to develop animal-free cheese using microbial casein
The German cheese maker Hochland Group has partnered with the Belgian-Dutch company Those Vegan Cowboys. They are jointly exploring the production of animal-free cheese, focusing on semi-hard and hard varieties that use microbial casein.
Microbial casein, produced through precision fermentation, is said to use only one-fifth of the resources (land and water) required by dairy farming. This method drastically reduces environmental impact, including an 80% drop in CO₂ emissions and elimination of methane.
Since microbial casein is considered a novel food, regulatory approvals will be required before it can be sold. The Vegan Cowboys expect to file for market approval in the United States this year. The first cheese tastings are scheduled in the Netherlands later this year to prepare for the product's market launch.
Source: vegconomist
🇳🇱 Mosa Meat filed a novel food regulatory application for its cultivated beef fat in the EU
The Dutch startup aims to introduce cultivated beef fat as an ingredient for blended meat products like burgers, meatballs, and empanadas. If approved, the product could be sold across the EU’s 27 member states and three EEA countries.
The EU's complex and stringent novel food regulatory framework involves evaluations by the European Commission, member states, and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), taking up to 18 months. Unlike Singapore, where full products can be submitted, the EU requires individual ingredient submissions.
Mosa Meat selected fat as its first focus due to its key role in delivering flavour, aroma, and mouthfeel—areas where plant-based alternatives often fall short. Cultivated fat helps bridge the sensory gap between traditional meat and plant-based options.
Source: Green Queen
🇸🇬 Umami Bioworks introduced cultivated caviar for high-end restaurants, retailers and consumers
The Singapore-based cultivated seafood pioneer’s new product is a hybrid caviar alternative that blends cultured sturgeon cells with plant-based ingredients. The product is tailored for the upscale dining and retail sectors and provides a sustainable luxury option.1
The product aims to address ethical concerns and environmental impacts tied to traditional caviar, such as overfishing and the endangerment of sturgeons, 90% of which are critically endangered.
The cultivated caviar is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and micronutrients while maintaining the taste and texture of traditional caviar, appealing to premium culinary markets.
Source: Green Queen
More buzzes
🇨🇳 Chinese manufacturer Angel Yeast completed the construction of a new industrial yeast protein production facility. The plant will be able to produce 11,000 tons of high-quality yeast protein per year. It will begin operations later in 2025. (vegconomist)
🇺🇸 InnerPlant’s InnerSoy, which uses fluorescent proteins to signal early signs of stress in soybeans, completed the FDA's New Protein Consultation. Its genetically engineered ‘sensor plants’ fluoresce under stress from pests, disease, or environmental threats, enabling early problem detection for farmers. (AgFunder)
🇨🇭 Certification body V-Label has introduced C-Label, a global accreditation system for cultivated meat. The goal is to build consumer trust in cultivated meat. The certification ensures transparency and adherence to robust global cell-based product production and distribution standards. (Green Queen)
BIO BUCKS
🇨🇦 The51 Food and AgTech Fund announced a $51M final close of its early-stage VC fund to back diverse founders innovating in agriculture
The fund targets deep science and advanced technologies, such as AI, robotics, and biotechnology, to address food security, crop resilience, and environmental sustainability.
The51 Food and AgTech Fund prioritizes diversity in its investment approach. It focuses on supporting women and underrepresented founders who have the potential to develop transformative agricultural technologies.
Despite challenges in the venture capital market, the fund’s successful closing signals strong trust in its ability to drive meaningful advancements in agritech. ATB Financial has a long history of supporting Alberta’s agriculture ecosystem, and its involvement underscores the fund’s credibility and growth potential.
💰 Investors: ATB Financial, Farm Credit Canada, Alberta Enterprise Corporation, National Bank of Canada, and more.
Source: Cision
🇮🇱 Pluri secured a $6.5M private investment led by Alejandro Weinstein and acquired a majority stake in cultivated cacao startup Kokomodo
Alejandro Weinstein, who previously led CFR Pharmaceuticals to a $3.2 billion acquisition by Abbott Laboratories in 2014, will also join Pluri’s Board of Directors, bringing valuable strategic insight beyond the funding contribution.
Pluri is acquiring a 71% stake in Israel's Kokomodo, which specializes in cultivated cacao production. This $4.5 million deal, involving 976,139 Pluri shares, diversifies into sustainable food technologies and complements Pluri’s other subsidiaries, such as Ever After Foods and Coffeesai.
Both the investment and acquisition are subject to regulatory approvals, including those from the European Investment Bank, Nasdaq, and the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange. The Kokomodo transaction is anticipated to close in Q2 2025.
Source: vegconomist
🇺🇸 Nexture Bio acquired Matrix Food Technologies to enhance capabilities in cultivated protein production
Matrix F.T. specialises in plant-based, edible nanofiber scaffolds and microbeads for cultivated protein production. The acquisition merges Nexture Bio’s capabilities with Matrix F.T.'s animal-component-free product innovations, advancing cultivated protein solutions.
Nexture Bio, established by the Generation Food Rural Partners Fund in 2023, develops scaffoldings for whole-cut products and other cultivated meat technologies. It recently launched a microcarrier product and is working on scaling up production with a GMP facility in California.
By merging Matrix F.T.’s IP, such as patents and trade secrets, with its proprietary technology, Nexture Bio can offer a broader range of high-performing adherent cell culture products aimed at global food and life sciences customers.
Source: vegconomist
🇺🇸🇫🇷🇭🇺 Pictor Biotech acquired GPC Bioand Eleszto Genetika to build a vertically integrated synthetic biology and biomanufacturing company
Pictor Biotech, formed last fall to acquire Solar Biotech's assets, has now acquired GPC Bio (France) and Eleszto Genetika (Hungary). This new entity merges Solar Biotech’s precision fermentation, Eleszto Genetika’s strain engineering, and GPC Bio’s facility design and automation.
With over 100 engineers, scientists, and executives, the company offers expertise to overcome industry hurdles like restrictive intellectual property and the complexities of scaling bioprocesses. It offers end-to-end solutions, from strain development to large-scale biomanufacturing deployment.
Leaders from the three firms remain in their roles to maintain operational continuity and client relationships.
Source: AgFunder
GEEK ZONE
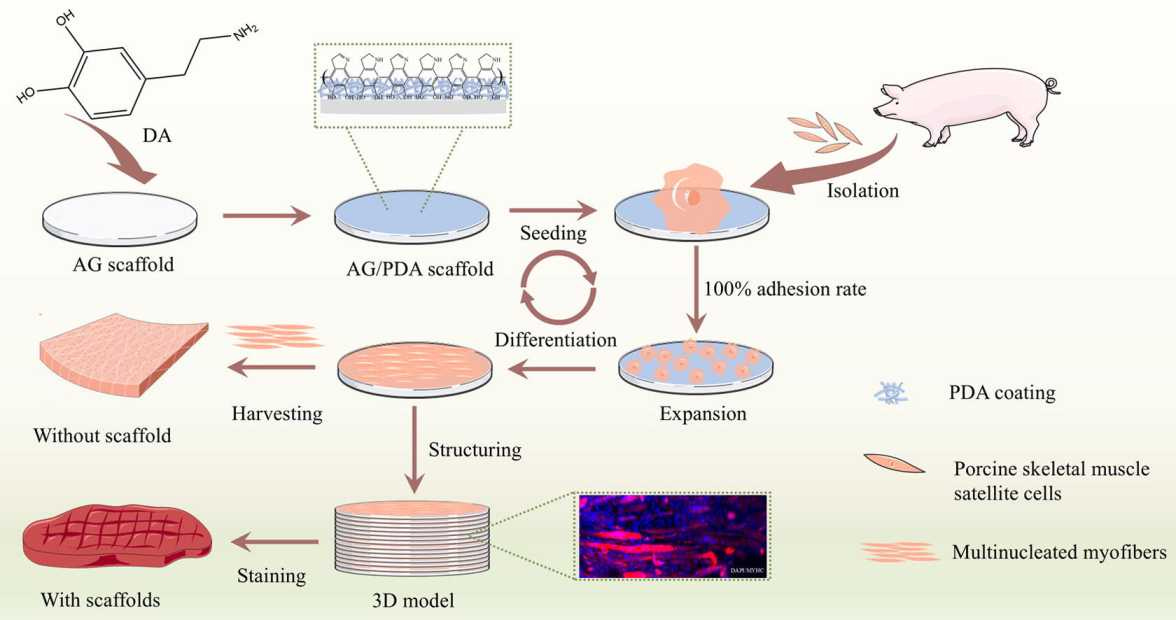
🐷 Mussel-inspired agarose scaffold provides an effective multifunctional platform for the in vitro fabrication of cultivated meat
The study used a novel agarose-based scaffold enhanced with a polydopamine (PDA) coating, which significantly improved cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation. The scaffold facilitates the creation of structured cultivated meat by promoting the development of protein-rich myofibers.
Agarose, a naturally abundant polysaccharide, was used due to its cost-effectiveness and gelation properties. PDA, inspired by mussel adhesion properties, boosts biocompatibility and bioactivity without toxic additives or proteins.
The reusable scaffolds, compatible with steam sterilization, facilitate large-scale cultivated meat production. They mimic the extracellular matrix, promoting muscle cell growth and differentiation. They have potential uses in fish, bovine, and chicken cell cultures.
Source: Journal of Advanced Research
🍅 Microalgae-based biofertilizers significantly enhanced soil fertility and microbial communities, promoting tomato growth
Combinations of microalgal strain (Tribonema sp.), shell powder, straw fermentation liquid, and agroforestry microorganism (Bacillus sp.) increased available phosphorus by 27.4%, dissolved organic carbon by 231.3%, and dissolved organic nitrogen by 403.4%.
The treatment also increased beneficial soil microbes like Thermonaerobaculia, Sordariomycetes, and Microascaceae, while reducing harmful pathogens like Pseudomonas and Togniniaceae.
These biofertilizers mitigated salinity issues, a major barrier to continuous cropping. Meanwhile, an increase in magnesium content by 73.4% improved plant resilience.
Source: Frontiers of Plant Science
🌽 CRISPR-Cas9-mediated editing of ZmPL1 gene improved tolerance to drought stress in maize
ZmPL1, a phylloplanin-like gene, negatively regulates drought tolerance by promoting reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation and lowering antioxidant enzyme activity. This impacts the plant's ability to manage oxidative stress.
Gene-edited maize plants displayed improved stress-related biochemical indicators, such as reduced malondialdehyde (MDA) and ROS. Proline accumulation, a key osmoprotectant, was higher in gene-edited plants, supporting better stress adaptation and cellular integrity under drought.
The study confirmed ZmPL1's interaction with the abscisic acid (ABA) pathway. Editing the ZmPL1 gene increased ABA levels under drought stress, improving physiological responses such as stomatal closure to reduce water loss.
Source: GM Crops & Food
🔬 Random peptide mixtures offer a non-antibiotic solution to microbial contamination in cultivated meat
Random peptide mixtures (RPMs), composed of random synthetic peptides, showed potential as non-antibiotic antimicrobial agents for cultivated meat, providing strong bactericidal activity, especially against Gram-positive bacteria, without significant cytotoxicity to mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs).
RPMs are less likely to develop bacterial resistance than traditional antibiotics. They do not induce the expression of inflammatory genes in MSCs, and their components are rapidly broken down during digestion, thereby reducing the risks of antimicrobial residues in food products.
By reducing reliance on antibiotics and traditional farming, RPMs in cultivated meat address concerns about the transmission of zoonotic diseases and the environmental damage caused by traditional meat production.
Source: Food Chemistry: Molecular Sciences
EAR FOOD
🎧 What are the traits that set winning agritech companies apart?
Operational and financial discipline: Companies thriving in today’s market often demonstrate strong financial discipline, focusing on profitability or achieving “default alive” status (where they can maintain operations without external funding). This is particularly crucial during periods of limited capital availability.
Strategic market and customer selection: Many standout companies avoid overextending geographically or diversifying too quickly. Instead, they concentrate on specific regions, customer profiles, or product categories to establish a strong foundation before scaling.
Systems thinking and innovation: Leaders in agritech often take a holistic approach, considering the broader system in which their solutions operate. This includes designing business models that align with the full supply chain and addressing regulatory or logistical barriers that might impede adoption.
BETTER BIOECONOMY EXCLUSIVE
💬 My recent conversations with bioeconomy innovators
Founder of Media City Scientific, Katie Bashant Day: A Scientist-Founder’s Journey to Make Biotech Research Reliable and Ethical
Innovation Specialist at The Good Food Institute India, Devika Suresh: Laying the Foundation for Smart Protein Leadership in India
Biotech consultant and ex-CSO of Vow, James Ryall: Bridging Science and Business to Support Startups Using Biomanufacturing
Check out more conversations!
🙌🏾 Want to get in front of an engaged, highly niche audience of 1,000+ biotech x agrifood enthusiasts?
Whether you’re announcing breakthroughs or exploring sponsorship opportunities, reach out at eshansamaranayake@gmail.com or reply to this email to get in touch.
Enjoyed this issue? If it brought you value, please consider sharing it with a friend who might benefit, or making a small pledge to acknowledge the hours behind each piece. Thank you for reading and supporting my work!
Disclaimer: Better Bite Ventures, where I work, is an investor of Umami Bioworks.