Expanding Asia’s Biomanufacturing Capacity, Egg Proteins From Potatoes, and Indian Alt Protein Adoption
Also: Turning food waste into alt fats
Hi, welcome to issue #58 of the weekly newsletter. Thanks for being here!
Here’s my favourite quote that I came across this week:
“All of climate investing is very long term. Biotechnology is mostly very long-term. Robotics is the same way… You don’t launch a project overnight and become a success like you’re a consumer app. That happens occasionally in software, but most things are hard. I like to say not all hard things are valuable, but most valuable things are really hard.”
- Khosla Ventures founder, Vinod Khosla
Alright, let’s dig into the latest developments in biotech-enabled food innovation! 🍽
BIO BUZZ
🇸🇬 ScaleUp Bio announces partnerships with Allozymes and Algrow Biosciences, plus LOIs with Terra Bioindustries and Argento Labs
The Singapore-based contract development and manufacturing organisation (CDMO) offers up to 10,000 L of fermentation capacity at its pilot-scale manufacturing facility. It’s one of the few globally that supports pilot-stage manufacturing with comprehensive services, including Asian market entry support.
The partnerships aim to use microbial and precision fermentation for food sustainability. Allozymes focuses on enzymatic solutions, and Algrow Biosciences is working on producing protein pigment from microalgae on a pre-commercial scale.
Letters of Intent (LOI) with Canada’s Terra Bioindustries and the UK’s Argento Labs are extending ScaleUp Bio's global reach by focusing on upcycling agri-food by-products and using biotechnology for product creation, respectively.
Source: Food Ingredients First
🐟 Aqua Cultured Foods collaborates with Ginkgo Bioworks to optimise the production of fermentation-derived whole-cut seafood
By using Ginkgo Bioworks’ cell programming platform, Aqua Cultured Foods can improve its microbial fermentation technology to produce seafood analogues with similar taste, texture, and appearance as conventional seafood.
Ginkgo Bioworks will use its cell programming platform, high throughput sequencing, and analytics to enhance and scale up Aqua Cultured Foods’ product quality, consistency, and manufacturing processes.
Aqua Cultured Foods is launching products, including tuna and scallops, with a six-week freshness guarantee and a minced shrimp variant. The startup is set to debut its products in Chicago's Michelin-starred restaurants this spring.
Source: Green Queen
🥔 PoLoPo’s molecular farming technology uses genetically engineered potatoes to produce egg proteins
The Israel-based startup’s protein production platform, called SuperAA, grows proteins inside a potato's tuber. It’s then harvested and extracted into protein powder.
Molecular farming has become more popular recently due to its promise of cost savings and efficiency. By turning plants into mini bioreactors, this technique allows for the scalable and cost-effective production of proteins using traditional crops.
PoLoPo believes the increasing demand for egg-derived ingredients such as ovalbumin, which improves food texture and shelf life, highlights their system’s potential. This comes amid a shortage of such ingredients, worsened by avian flu outbreaks and rising production costs.
Source: The Spoon
🥛 Imagindairy and Ginkgo Bioworks team up to optimise the development of animal-free non-whey dairy proteins
The multi-year program is funded in part by a joint grant from the Board of Governors of the Israel-U.S. Binational Industrial Research and Development (BIRD) Foundation.
US-based Ginkgo will apply its AI and Foundry capabilities to engineer biological systems that offer better production economics and functionality for non-whey dairy proteins.
Imagindairy is responsible for developing the production process and handling the scale-up and manufacturing of these proteins. The Israeli company aims to supply food producers with a comprehensive array of animal-free dairy proteins.
Source: PR Newswire
🇳🇱🇸🇬 The Protein Brewery has received approval from the Singapore Food Agency for its mycelium-derived ingredient, Fermotein
This allows the Dutch fermentation specialist to import, manufacture, and sell Fermotien or products containing it while expanding its operations in the country. Fermotein has also achieved GRAS status in the US.
Fermotein is produced through biomass fermentation of edible fungal species, transforming sugars into a complete protein. The product is said to offer a neutral flavour and authentic texture in products ranging from baked goods to alternative meat and dairy
Fermotein can be produced globally on a local scale using non-allergenic crops like corn, potatoes, cassava, and sugar beet as feedstock.
Source: vegconomist
MACRO STUFF
🇮🇳 F&B launches with alt protein in India increased at a CAGR of 11% between 2019–2023 but challenges remain
Companies are localising flavours to cater to Indian tastes. They recognise the importance of integrating alt proteins into familiar dishes to appeal to the country's growing middle class and promote mainstream adoption.
The alt protein industry faces significant challenges in mimicking the texture and taste of traditional meats, especially seafood. Efforts are focused on extensive R&D and approaches like high- and low-moisture extrusion.
Alt proteins in India are currently more expensive than animal meats. This is mainly due to higher taxes for plant-based alternatives, lower tax rates and subsidies for animal meats, and the need to import key ingredients.
Source: Food Ingredients First
💡 McKinsey survey shows that the majority of US consumers are open to trying foods with novel ingredients
More than half are willing to pay extra for them. Over one-fifth are willing to pay up to 4x as much if a product features a novel ingredient. Health benefits and sustainability are significant motivators for trying these ingredients.
Using familiar terminology and well-understood nutritional statements about potential health impacts (such as “good or complete source of protein”) are most compelling for the consumer.
Consumers' willingness to try novel ingredients varies by time of day. There is a higher willingness to try them as lunch options and on-the-go snacks compared to other meal times.
Source: McKinsey
💬 Aleph Farms’ CEO expresses regret that the cultivated meat industry didn't manage public expectations better from the start
Didier Toubia acknowledged the gap between industry insiders' optimism and public expectations. He pointed out that the industry faces significant challenges, including regulatory hurdles, high production costs, and the need for strategic differentiation—similar to the early obstacles faced by the EV industry.
Cultivated meat companies are innovating by developing dedicated food-grade supply chains and adopting new processes tailored for food applications. They're also adapting their scale-up strategies in response to a difficult funding landscape.
Despite scepticism, the cultivated meat sector is a long-term play that requires continuous evolution and adaptation. Companies are focused on gradually scaling up, with an eye on eventually achieving widespread commercialization and profitability.
Source: Fast Company
🚀 Despite a significant drop in agrifood tech funding, Vinod Khosla and Dave Friedberg remain optimistic about exceptional founders
Vinod Khosla expressed scepticism towards the economic viability of cultivated meat. He revealed that none of the two dozen business plans reviewed by Khosla Ventures made economic sense.
Dave Friedberg spoke about the rapid advancements in technologies such as predictive modelling, data generation from biological systems, automation, and machine vision. These advances significantly improve productivity and economic viability in agriculture and beyond.
Vinod Khosla argues that venture capital, contrary to common perception, is well-suited for agrifood tech due to its long-term investment strategy focused on real technological innovations.
Source: AgFunder
📉 Climate change and extreme weather events are projected to drive up food prices
The study by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research and the European Central Bank in Germany analyzed over 27,000 data points from consumer price indexes and weather data across 121 countries over 30 years. It linked climate shocks to inflation and food cost increases.
It found that in the worst-case scenario, food costs could rise by 3.2% annually and overall inflation by up to 1.2%. In best-case scenarios, food inflation is expected to increase by 0.9% annually until 2035, with overall inflation rising by up to 0.3%
The research indicates that both excess heat and wet conditions due to climate change can significantly affect food inflation, with these impacts lasting up to a year.
Source: Green Queen
JOIN EUROPE’S LARGEST CLIMATE TECH GATHERING
The HackSummit, Europe’s largest gathering of ClimateTech builders and investors returns to Lausanne Switzerland on June 13-14th for two days of networking and deal-making.
👀 See the full lineup of speakers here.
Use the code BetterBioeconomy20 to save 20% on your pass!
BIO BUCKS
🇩🇪 Innocent Meat secured €3M to develop an automated plug-and-produce solution for cultivated meat
Innocent Meat's model provides food producers with essential equipment like growth media, cell lines, and manufacturing hardware. The equipment allows clients to safely and efficiently oversee cultivated meat production.
With the fresh capital, the German startup will develop biocomponents, scale up its pilot plant, and initiate certification processes.
Innocent Meat is developing a production model based on a platform that uses stem cells to replicate animal muscle and fat tissue. The startup has created a serum-free medium to grow these cells for its cultivated pork.
Source: vegconomist
🇬🇧 Clean Food Group received an additional £2.5M to accelerate the commercialisation of sustainable oils and fats
The proprietary technology platform uses yeast strains and fermentation, using food waste as its feedstock, to produce sustainable alternatives to traditional oil and fat ingredients.
The UK-based company’s flagship product is a sustainable alternative to high oleic palm oil. An externally validated LCA shows a 90% reduction in greenhouse gases compared to traditional palm oil.
The alternative oil is versatile and suitable for use in baked goods, confectionery, and cosmetics. It serves as a direct substitute for traditional oil and fat ingredients.
Source: Cell Base
SOCIAL FEAST
🤩 Novel food tech could scale the production of high-value agricultural products with less exploitation than traditional methods
Industries like sugar, coffee, chocolate, and animal agriculture, have a history of exploitative practices. However, replacing traditional industries with novel food technologies is challenging due to the region-specific nature of climate, soil, and knowledge.
There are glimmers of hope with initiatives such as POSEIDONA's upcycling of invasive seaweed and algal side streams, Day 8's harvesting of Rubisco from unused crop leaves, and RESPECTfarms' focus on growing cultivated meat in conventional animal ag facilities.
Upskilling billions of people is a daunting task. Maya uses the example of a former coal miner who went out of business trying to transition to hemp-based farming. It underscores the complexities of transitioning from traditional industries to novel ones.
Source: Maya Benami
😐 Food system accounts for 22% of GHG emissions, but solutions only receive 6% of VC funding
Meat and dairy alternatives offer significant GHG reduction benefits per VC dollar invested. They achieve 3x the GHG reduction of green concrete and 11x that of EVs.
In 2022, alternative proteins received $4.4B in global funding. This is significantly less than the $38B in subsidies that meat and dairy industries receive annually in the US alone.
The potential of plant-based, cell-based, and fungi-based foods to transform human and planetary health underscores the urgency of increasing funding for these solutions.
Source: Nathan Paumier
🤣 For the lolz

MORE ON BETTER BIOECONOMY
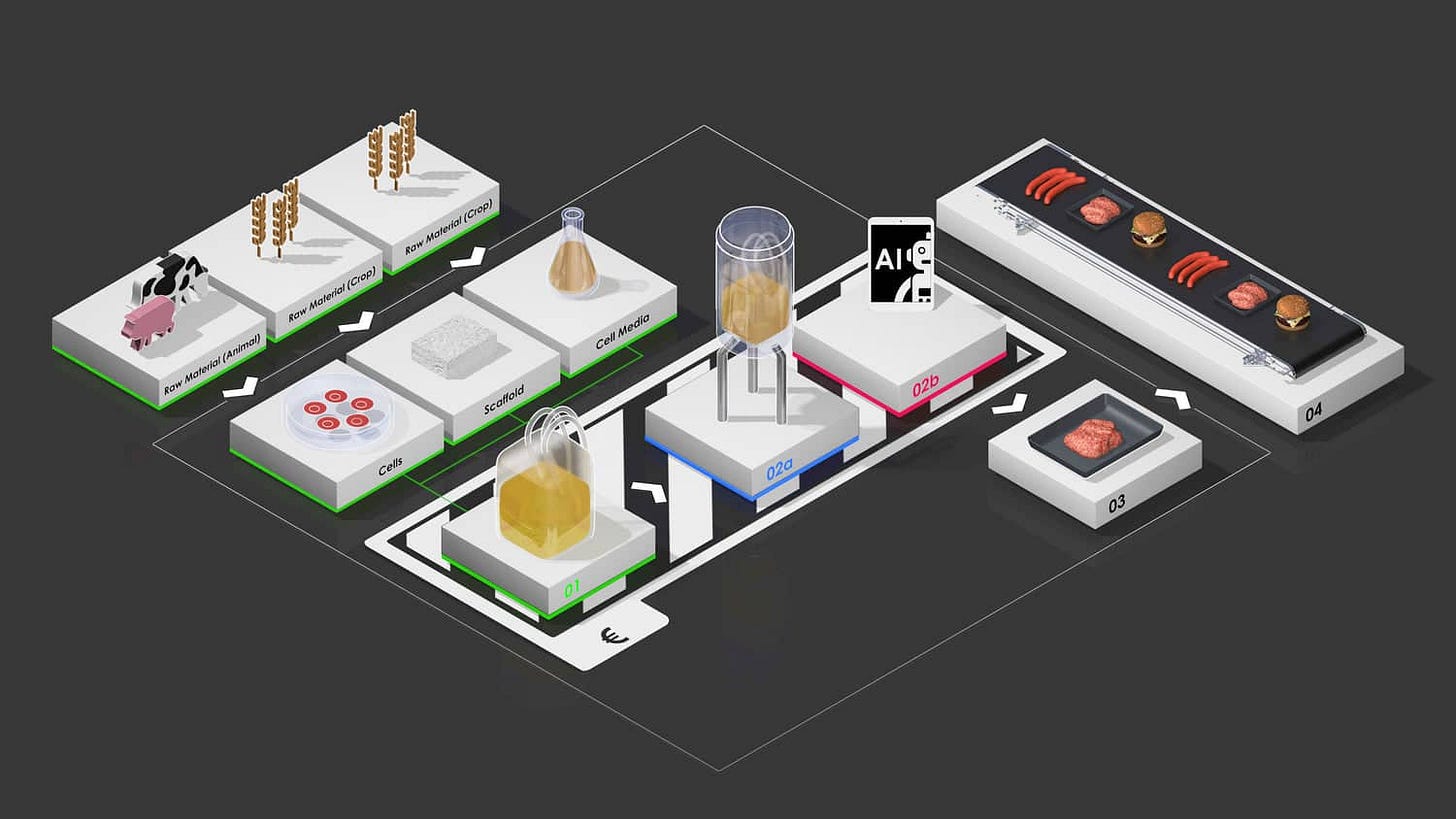
🎙 My Q&A with Synonym's co-founder, Joshua Lachter: Financing and developing infrastructure for the bioeconomy
What you can learn from this article
How Synonym empowers companies to bring bioproducts to market
Inspiration behind Synonym and the mission
Biggest challenges in biomanufacturing and how Synonym addresses them
What makes food biomanufacturing different from pharma in terms of economics
Why APAC’s fermentation capacity is trailing behind and if it's expected to improve
Sources of funding to increase biomanufacturing capacity
Source: Better Bioeconomy
That’s a wrap. Thank you for taking the time to read this issue!
Are you new here?
Know anyone else who would dig this newsletter?






Super cool article - I'm surprised to see the number of people willing to try new ingredients - thanks for sharing!
Excellent newsletter as always @Eshan! Thank you for featuring my post on alt protein funding